Road Network Partitioning for Recommender Systems
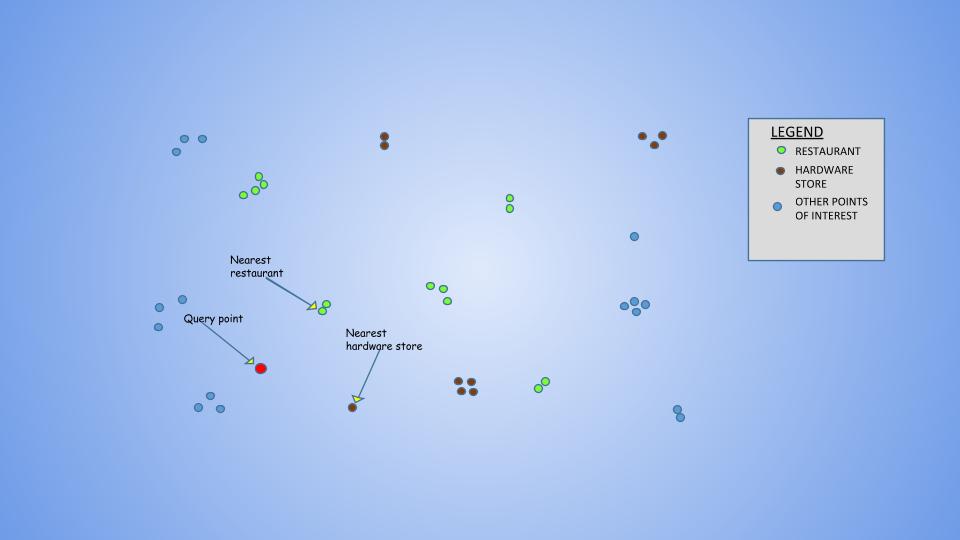
This project aimed at improving the scalability as well as the accuracy of the recommender systems using the aspect of locality of the user in Location Based Services - by dividing the road network into smaller partitions and processing relevant partitions for a given point of interest.
Recommender systems have been successfully used to provide items of interest to the user, from an overwhelming set of choices. However, where items being recommended have an associated location, by Tobler’s First Law of Geography, there is a general preference for things nearby. This aspect of locality can be leveraged not only to improve the quality and accuracy of recommendations, but also the scalability of the recommendation algorithm by suitably partitioning the road network used for travelling to the places being recommended.
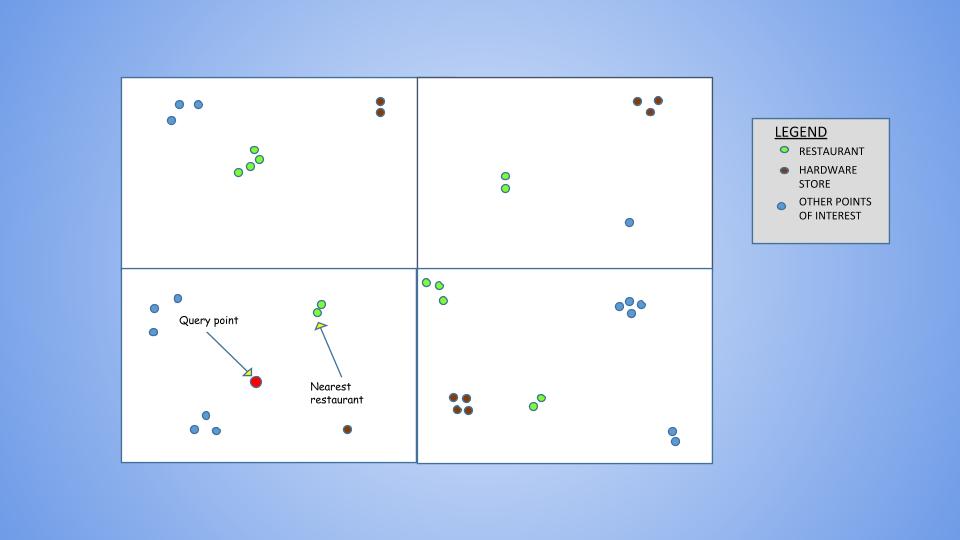
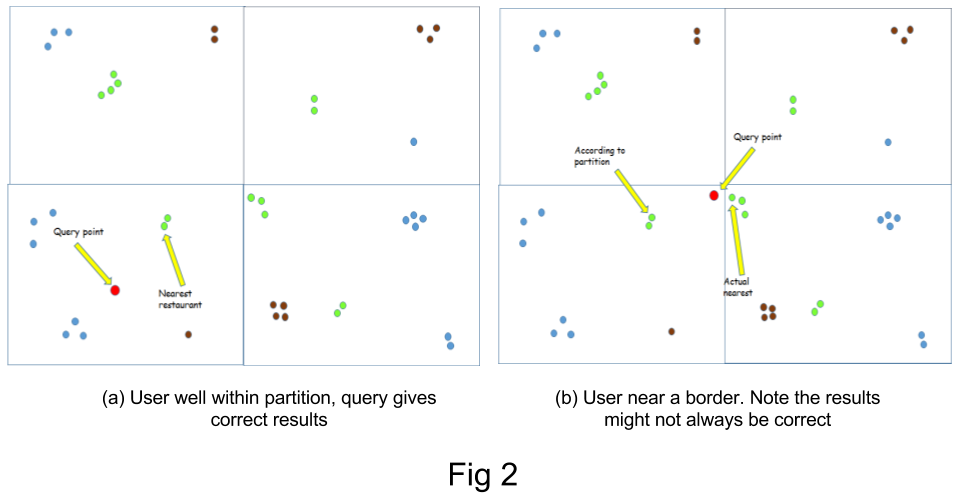
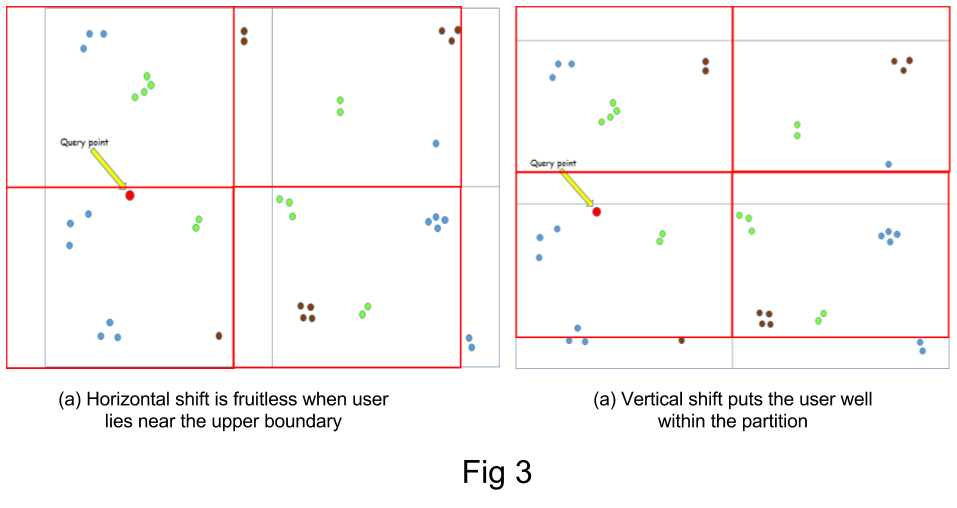
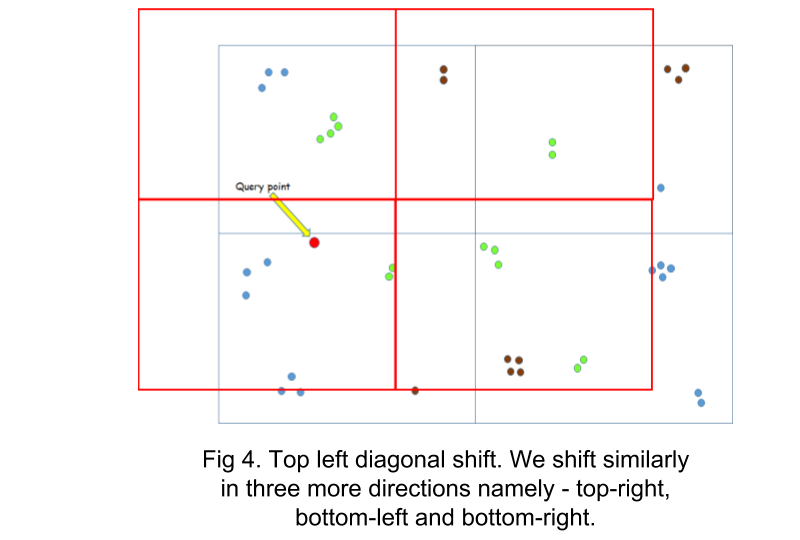
However, this method gives inaccurate results when the user lies near the boundary of a grid. This is due to the fact that the nearest POI could lie in a neighbouring grid, which would never be considered. To solve this limitation, the case when the user lies near a boundary is detected and the grids are shifted, in order to include the POIs that lie in the neighbouring grids. As shifting just horizontally or vertically does not work in all cases (see fig), the grids are shifted diagonally.